Abstract
This article provides a comprehensive introduction to Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) for beginners in the field of cybersecurity. It covers the fundamental concepts, benefits, related technologies, common products, and best practices for SIEM implementation. The article also discusses the importance of SIEM knowledge in various cybersecurity career paths and the evolving landscape of cyber threats. A live demonstration of Splunk, a popular SIEM tool, is included to provide practical insights.
Keywords: SIEM, cybersecurity, log management, threat detection, data analytics, IDPS, SOC, SOAR
Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, organizations face an ever-increasing number of cybersecurity threats. With cyberattacks occurring every 39 seconds (University of Maryland, 2017), the need for robust security measures has never been more critical. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) has emerged as a crucial tool in the cybersecurity arsenal, helping organizations detect, analyze, and respond to security threats in real-time.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive introduction to SIEM for newcomers to the field of cybersecurity. We will explore the core concepts of SIEM, its benefits, related technologies, common products, and best practices for implementation. By the end of this article, readers will have a solid foundation in SIEM and understand its importance in modern cybersecurity strategies.
Understanding SIEM
Definition and Core Concepts
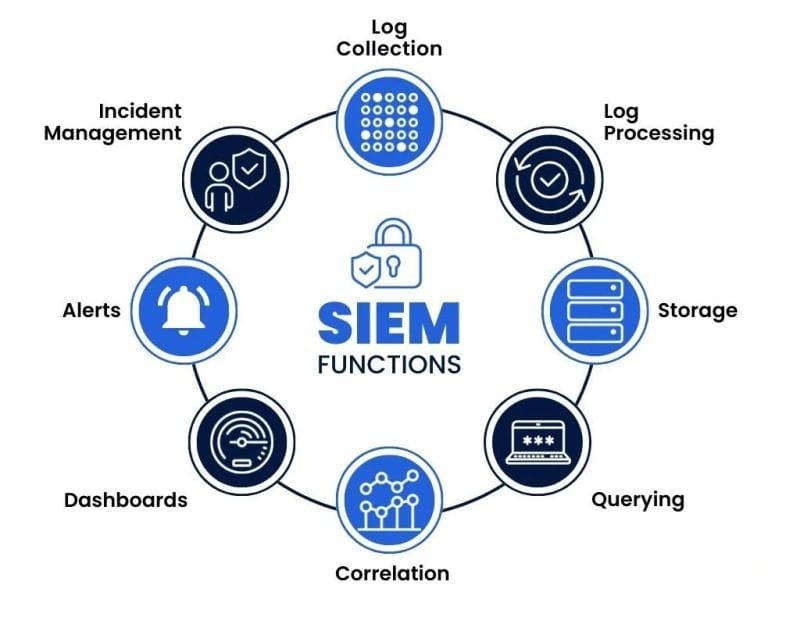
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) is a comprehensive approach to security management that combines two essential functions: Security Information Management (SIM) and Security Event Management (SEM) (Gartner, 2005). SIEM tools collect, analyze, and correlate security event data from various sources across an organization’s IT infrastructure to provide real-time analysis of security alerts.
The core concepts of SIEM include:
- Log Management: SIEM systems collect and aggregate log data from multiple sources, including network devices, servers, applications, and security tools.
- Normalization: The collected data is normalized into a standard format to enable effective analysis and correlation.
- Correlation: SIEM tools use rule-based or machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and relationships between different security events.
- Analysis: Advanced analytics capabilities help identify potential security threats and anomalies in real-time.
- Alerting: SIEM systems generate alerts when suspicious activities or potential security breaches are detected.
- Reporting: Comprehensive reporting features help organizations meet compliance requirements and improve their overall security posture.
Importance of SIEM
SIEM plays a crucial role in modern cybersecurity strategies for several reasons:
- Centralized Visibility: SIEM provides a single, centralized view of an organization’s security posture across its entire IT infrastructure.
- Real-time Threat Detection: By analyzing data from multiple sources in real-time, SIEM can quickly identify and alert on potential security threats.
- Compliance Management: SIEM tools help organizations meet various regulatory compliance requirements by providing detailed audit trails and reports.
- Incident Response: SIEM systems facilitate faster and more effective incident response by providing security teams with comprehensive, contextual information about security events.
- Historical Analysis: The ability to store and analyze historical data allows organizations to conduct forensic investigations and identify long-term trends in their security posture.
SIEM Benefits
Implementing a SIEM solution offers numerous benefits to organizations of all sizes:
Enhanced Visibility:
SIEM tools provide comprehensive coverage of an organization’s IT environment, offering visibility into security events across networks, applications, and systems. This enhanced visibility allows security teams to detect anomalies earlier and improve response times to potential threats.
Threat Intelligence:
By collecting and analyzing data from various sources across the organization, SIEM tools can detect suspicious activities and potential threats before they escalate into full-blown security breaches. This proactive approach to threat detection is crucial in today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape.
Compliance
SIEM solutions streamline compliance reporting by automatically generating reports from logged security events. This capability helps organizations meet various industry standards and regulatory requirements, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR.
Incident Management
SIEM tools improve incident management by providing real-time alerts to security teams when potential threats are detected. This enables rapid isolation and containment of security incidents, minimizing their impact on the organization.
Cost Savings
While implementing a SIEM solution requires an initial investment, it can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. By preventing costly data breaches and improving operational efficiency, SIEM can help organizations avoid the average cost of a data breach, which is estimated at $3.86 million (IBM, 2020).
Related Technologies
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) are crucial components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. IDPS works in conjunction with SIEM to safeguard digital assets by detecting and preventing unauthorized access or exposure.
There are five main types of IDPS:
- Network-based IDPS (NIDS)
- Host-based IDPS (HIDS)
- Wireless IDPS (WIDS)
- Network Behavior Analysis (NBA)
- Application Protocol-based IDPS
IDPS uses two primary detection methods:
- Signature-based Detection: Identifies known threats based on predefined patterns or signatures.
- Anomaly-based Detection: Detects unusual activities by comparing them to established baselines of normal behavior.
Best practices for effective IDPS deployment include:
- Understanding your environment
- Establishing a baseline of normal network behavior
- Managing false positives
- Ensuring regular updates and maintenance
Security Operations Center (SOC)
A Security Operations Center (SOC) is a centralized function within an organization that monitors networks, websites, databases, servers, and applications for security threats. SOCs often use SIEM tools as a core component of their operations.
Benefits of implementing a SOC include:
- Real-time monitoring and threat detection
- Incident response and recovery
- Threat intelligence gathering and analysis
- Compliance with regulatory requirements
- Reduced cost of security breaches
There are three main SOC models:
- In-house SOC
- Managed SOC (outsourced)
- Hybrid SOC
The choice of SOC model depends on an organization’s specific needs, resources, and security requirements.
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR)
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) is a technology that enhances SIEM capabilities by automating threat response, reducing alert fatigue, and providing a more complete security picture.
SOAR consists of three core components:
- Orchestration: Coordinating and managing various security tools and processes.
- Automation: Automating repetitive security tasks and workflows.
- Response: Facilitating rapid and effective incident response.
When implementing SOAR, organizations should consider factors such as:
- Ease of use
- Integration with existing security tools
- Workflow capabilities
- Deployment flexibility (on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid)
Common SIEM Products
There are several popular SIEM products available in the market, each with its own strengths and features:
IBM QRadar
IBM QRadar offers real-time threat detection and advanced analytics capabilities. It is particularly well-suited for large enterprises and integrates vulnerability scanning and patch management features.
Splunk Enterprise Security
Splunk Enterprise Security is known for its user-friendly interface and powerful data analysis capabilities. It provides real-time visibility into security events and uses machine learning for quick threat response. Splunk is suitable for organizations of various sizes.
LogRhythm
LogRhythm is a cloud-based SIEM tool that combines log management, security analytics, and incident response with automated workflows. It offers a unified platform for threat detection and response.
McAfee Enterprise Security Manager (ESM)
McAfee ESM provides real-time threat detection and security analytics with integrated threat intelligence feeds. It offers a comprehensive solution for enterprise-level security management.
ArcSight Enterprise Security Manager
ArcSight Enterprise Security Manager uses machine learning and behavioral analysis for advanced threat detection. It also features automated response workflows to streamline incident management.
AlienVault USM
AlienVault USM is a cloud-based SIEM tool that integrates log management, security analytics, and threat intelligence with automated response workflows. It is particularly well-suited for small to medium-sized organizations.
Splunk Enterprise: A Live Demonstration
Splunk Enterprise is one of the most popular SIEM solutions in the market. Here’s an overview of its key features and capabilities:
Main Dashboard
The Splunk Enterprise main dashboard provides a centralized view of security events and system performance. It offers quick access to various applications and tools, including:
- Search and Reporting
- Splunk Secure Gateway
- Upgrade Readiness App
Data Analysis and Visualization
Splunk allows for detailed data analysis and visualization through its powerful search and reporting capabilities. Users can:
- Filter events by timeframe
- Create custom searches and alerts
- Build visual reports using various chart types (e.g., bar charts, line graphs, pie charts)
Real-time Monitoring
Splunk excels at monitoring and analyzing real-time data from various sources, providing insights into:
- System events
- Security incidents
- Application performance
Customization and Alerts
Splunk offers extensive customization options, including:
- Pre-configured templates for reports and alerts
- Custom dashboard creation
- Ability to set up alerts for specific conditions or thresholds
SIEM Implementation Best Practices
To ensure a successful SIEM implementation, organizations should follow these best practices:
Establish Clear Objectives
Before implementing a SIEM solution, clearly define the requirements and objectives based on your organization’s business and security goals. This will help guide the selection and configuration of the SIEM tool.
Ensure Full Visibility
Review and map out all relevant data sources in your infrastructure to ensure comprehensive monitoring. This includes network devices, servers, applications, and security tools.
Conduct Research and Pilot Run
Thoroughly research SIEM products to find the best fit for your organization. Conduct a pilot run to test the chosen tool in a small subset of your environment before full deployment.
Establish a Baseline
Allow the SIEM system to run under normal operations for a period of time to establish a baseline for detecting deviations and anomalies.
Continuous Improvement
Regularly review threat data, fine-tune rules, and update the SIEM software to adapt to evolving threats and changing organizational needs.
Avoid Common Mistakes
Be aware of and avoid common SIEM implementation mistakes, such as:
- Lack of proper planning
- Failing to scope projects accurately
- Using a one-size-fits-all approach
- Lack of discrimination in monitoring
Career Opportunities in SIEM
Understanding SIEM tools and concepts is crucial for success in various cybersecurity roles. Knowledge of SIEM can lead to career opportunities such as:
- SOC Analyst
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Threat Intelligence Analyst
- Security Engineer
- Information Security Manager
- IT Security Consultant
To stay competitive in the job market, it’s essential to keep up with the latest trends and technologies in cybersecurity, including advancements in SIEM tools and practices.
Conclusion
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) has become an indispensable tool in modern cybersecurity strategies. By providing real-time threat detection, comprehensive log management, and advanced analytics capabilities, SIEM helps organizations protect their digital assets and maintain a strong security posture.
This article has provided a foundation in SIEM concepts, benefits, related technologies, and implementation best practices. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the importance of SIEM in safeguarding organizations will only grow. Cybersecurity professionals and aspiring practitioners should continue to expand their knowledge of SIEM and related technologies to stay ahead in this rapidly changing field.
References
- Gartner. (2005). Improve IT Security with Vulnerability Management.
- IBM. (2020). Cost of a Data Breach Report 2020.
- University of Maryland. (2017). Hackers Attack Every 39 Seconds.